Operator Library: Base
Library: Base
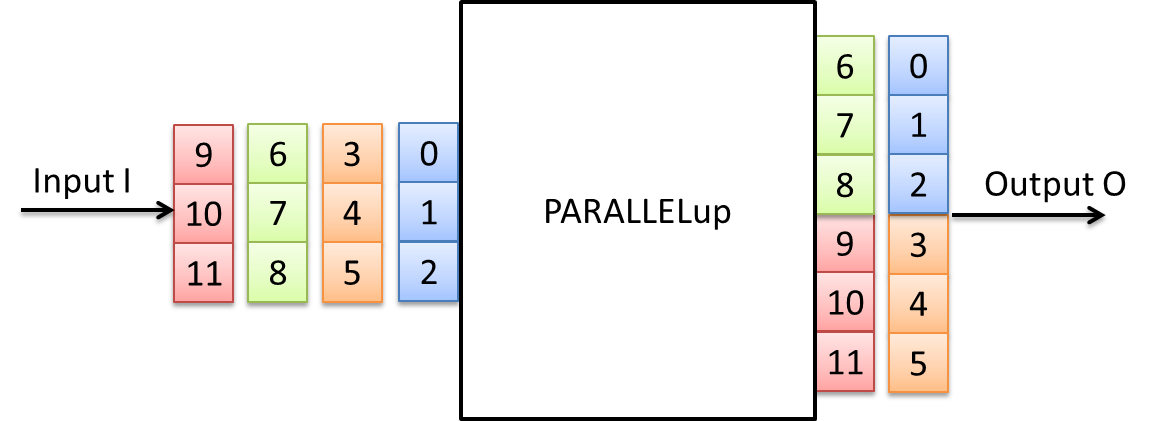
The operator PARALLELup increases the parallelism between the input link and the output link.
Following figure shows a parallel up conversion from parallelism 3 at the input to parallelism 6 at the output.
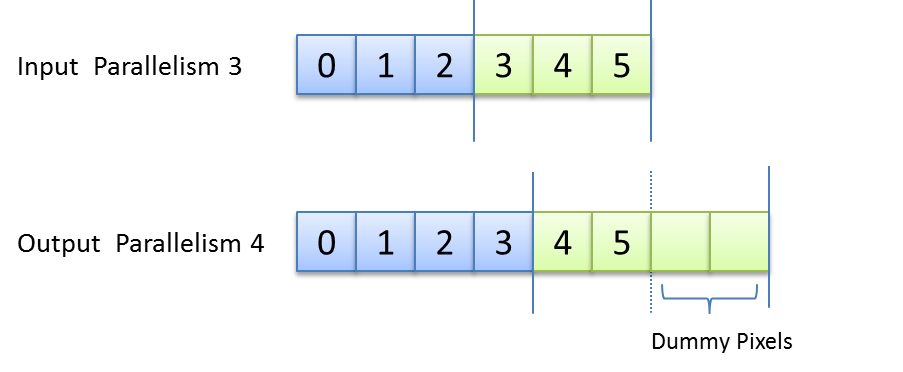
In VisualApplets, the width of an image line always has to be a multiple of the parallelism. As the PARALLELup operator allows any parallelism at its output it is possible that the width of an image line at the output is not a multiple of the output parallelism. In this case the operator will add dummy pixels to fill up the image line. The value of this dummy pixel is undefined. In VA simulation dummy pixels will be set to zero for better visibility.
The following figure shows in illustration of this dummy pixel insertion. As can be seen, the output parallelism of four cannot map the input line width of 6 pixels. Here, two extra dummy pixel are added so that the line width becomes eight.
The operator requires fewest resources if the output parallelism is an integer multiple of the input parallelism.
|
The range of the input bit width is [1, 64] for unsigned values. For signed inputs, the range is [2, 64]. For unsigned color inputs [3, 63] and for signed color inputs [6, 63]. |
|
|
The output image width must not exceed 2^31-1. The maximum image width at the output is automatically rounded to the next multiple of O.Parallelism. As a result, I.MaxImgWidth must not be greater than 2^31-1-O.Parallelism so that the rounded maximum image width at the output doesn't exceed 2^31-1. |
The use of operator PARALLELup is shown in the following examples:
-
Design Parametrization - Invalid link property.
-
'Color Plane Separation Option 2 - Three Buffers, One DMA'
Sequential output of the color planes using three image buffers and one DMA operator.
-
Sequential DMA output of the color planes. The color separations is performed using operator ImageBufferMultiROI. An additional pre-sorting optimizes the bandwdith and resources.
-
'Color Plane Separation Option 5 - Sequential Output with Advances Processing'
Example on separation of color planes. The RGB input is split into its component and sequentially output via one DMA channel. The splitting if performed by collecting same components in parallel words and reading with FrameBufferRandomRead.
-
Examples - Downsampling by factor 3x3 without the use of operator SampleDn.
-
'Functional Example for the FrameBufferMultRoiDyn Operator on the imaFlex CXP-12 Platform'
Examples - Demonstration of how to use the operator
-
Examples - Demonstration of how to use the operator


 Prev
Prev